Financing Options

Funding a coding bootcamp can seem daunting, but several options exist to make it more accessible. Understanding the pros and cons of each financing method is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with your financial situation and long-term goals. Careful consideration of interest rates and repayment terms is also vital to avoid unexpected financial burdens.
Bootcamp Payment Plans
Many coding bootcamps offer in-house payment plans. These typically involve splitting the total tuition cost into smaller, monthly installments over the duration of the program or a slightly extended period. This allows students to manage their expenses more effectively and avoid taking out external loans.
Pros: Often the simplest option, with no credit check or additional fees beyond the tuition. It allows for budgeting and predictable monthly payments. Cons: Payment plans may not offer the same flexibility as loans; the total cost remains the same, regardless of your financial situation. Interest is usually not charged, but the lack of flexibility is a drawback for students who might experience unforeseen financial challenges.
Personal Savings
Using personal savings to fund a coding bootcamp offers the most straightforward financial approach. This method avoids debt and interest payments entirely.
Pros: No debt, no interest, complete financial control. Cons: Requires significant upfront savings; may delay enrollment if sufficient funds aren’t available. This option isn’t feasible for everyone.
Loans
Several types of loans can finance coding bootcamps. These include personal loans from banks or credit unions, federal student loans (in some cases), and bootcamp-specific financing partners. Interest rates and repayment terms vary significantly depending on the lender and the borrower’s creditworthiness.
Pros: Access to funds for those lacking sufficient savings. Cons: Accumulation of debt and interest payments, which can significantly increase the overall cost. Credit checks are usually involved, and poor credit can lead to higher interest rates or loan denial.
Scholarships and Grants
Coding bootcamps and various organizations offer scholarships and grants to deserving students. These are often merit-based, considering factors such as academic performance, demonstrated financial need, or commitment to specific fields.
Pros: Can significantly reduce or eliminate the cost of tuition. Cons: Competition for scholarships can be intense; eligibility criteria may restrict access for some applicants. Finding and securing scholarships requires dedicated research and application efforts.
Steps to Apply for a Bootcamp Loan
Applying for a bootcamp loan generally involves these steps:
- Research lenders: Explore various lenders offering educational loans, comparing interest rates, repayment terms, and fees.
- Check your credit score: A higher credit score generally leads to more favorable loan terms.
- Complete the loan application: Provide necessary personal and financial information.
- Provide documentation: This usually includes proof of enrollment, income verification, and potentially other supporting documents.
- Review loan terms: Carefully review the loan agreement before signing to understand all fees, interest rates, and repayment schedules.
- Accept the loan and begin repayment: Once approved, you can access the funds and begin making payments according to the agreed-upon terms.
Program Length and Intensity: How Much Does A Coding Bootcamp Cost
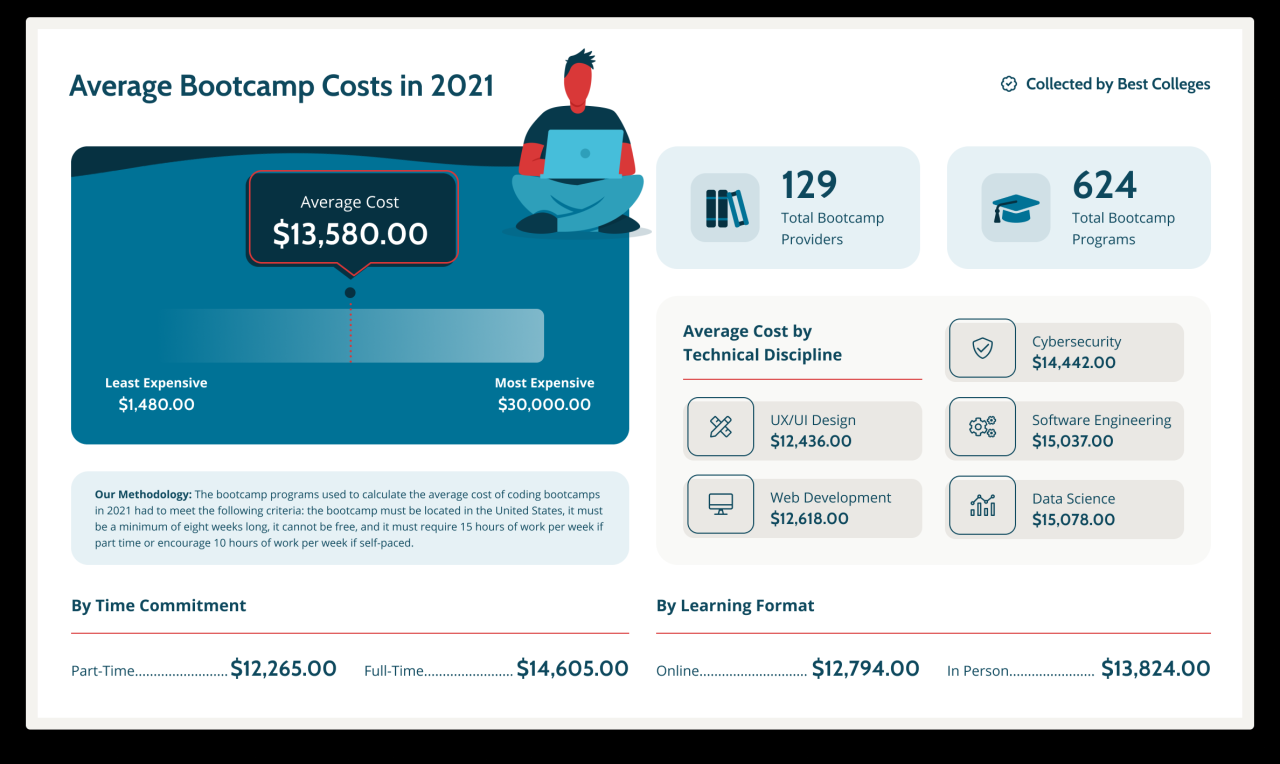
The duration and intensity of a coding bootcamp significantly impact its overall cost. Longer programs generally cost more, while full-time programs tend to be pricier than part-time options due to the accelerated learning pace and increased instructor support. Understanding this relationship is crucial for making an informed decision about which program best suits your budget and learning style.
Program intensity, measured by the number of hours dedicated to learning per week, directly affects the price. Full-time bootcamps typically involve 40-60 hours per week, demanding a significant time commitment and resulting in a faster completion time, but at a higher cost. Part-time bootcamps, on the other hand, might only require 10-20 hours per week, extending the program’s length and reducing the overall weekly cost but increasing the total cost due to the longer program duration.
Program Length and Cost Relationship
The cost of a coding bootcamp is directly proportional to its duration. A shorter, more intensive program will pack the same amount of material into a compressed timeframe, potentially resulting in a higher cost per week but a lower overall cost. Conversely, a longer, less intensive program spreads the cost over a longer period, resulting in a lower weekly cost but a higher overall cost. For example, a 12-week full-time bootcamp might cost $12,000, while a 24-week part-time program covering the same material could cost $15,000. While the part-time option costs more overall, the weekly or monthly cost is lower.
Intensity and Pricing, How much does a coding bootcamp cost
Full-time bootcamps, due to their accelerated nature, often command higher tuition fees. This is because they require more intensive instructor support, more resources, and often include career services packages. Part-time programs, while less expensive per week or month, require a longer commitment, potentially leading to higher overall costs. The higher cost of full-time programs reflects the increased intensity of the learning experience, the concentrated delivery of the curriculum, and the faster job placement support typically offered.
Cost-Effectiveness Comparison
The most cost-effective program depends on individual circumstances. For students who can dedicate themselves full-time to learning, a shorter, full-time program might be more financially efficient due to its lower overall cost. However, for those with existing job commitments or other responsibilities, a part-time program, despite its higher overall cost, might be more practical and ultimately more cost-effective because it allows them to maintain income while learning.
Cost Per Week/Month for Various Programs
| Program Type | Duration (Weeks) | Total Cost (USD) | Cost Per Week (USD) | Cost Per Month (USD) (assuming 4 weeks/month) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full-time Intensive | 12 | 12000 | 1000 | 4000 |
| Full-time Standard | 16 | 16000 | 1000 | 4000 |
| Part-time | 24 | 15000 | 625 | 2500 |
| Part-time Extended | 36 | 18000 | 500 | 2000 |

Tim Redaksi